Siqi Shi
EXTENDED ABSTRACT: Data-driven machine learning (ML) has showed excellent capabilities in materials propertyprediction and novel materials discovery, whose upper limitation of the performance of ML models is determined by thequality of the input data. Due to the characteristics of materials data such as multiple sources, small-size samples and high-dimensionality feature space, different structures, and stronguncertainty, it is difficult to ensure its integrity, consistencyand accuracy, which can introduce undesirable bias for MLmodeling. Focusing on the quality and quantity of material data,this report proposes a new method of data quality governancedriven by both data and knowledge, based on the ML frameworkwith domain knowledge embedding, to provide an effectivestrategy for solving the problem of materials data governanceMoreover, the work of the research group in data qualitygovernance and its application embedded in domain knowledgewill be introduced and prospected for mining creep structure-activity relationship of nickel-based single crystal superalloys and predicting the activation energy of solid electrolyte materials for energy storage battery.
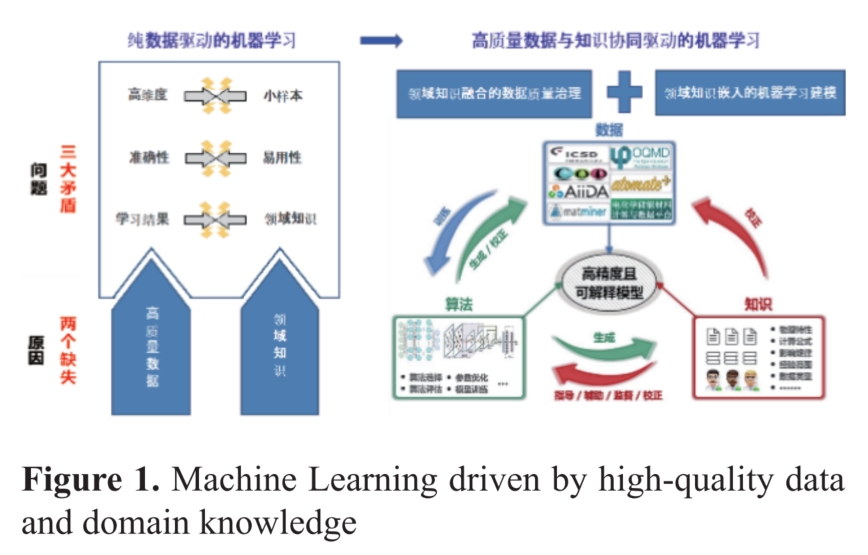
Keywords: Data quality; Machine Learning; Domain Knowledge; Materials Property Prediction; Novel Materials Discovery
REFERENCES
[ l] Yue Liu, Zhengwei Yang, Xinxin Zou, Shuchang Ma, Dahui Liu, Maxim Avdeev, Siqi Shi, Data Quantity Governance for Machine Leaming in Materials Science [J]. NATL SCI REV, 10(7), (2023) nwad125.
[2] Yue Liu, Zhengwei Yang and Zhenyao Yu et al. Generative Artificial Intelligence and Its Applications in Materials Science: Current Situation and Future Perspectives. J. Materiomics, 9(4), (2023) 798-816.

Siqi Shi obtained his B.S. and M.S. degrees from Jiangxi Normal University in 1998 and in 2001, respectively. He got his Ph.D. degree from Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2004. After that, he joined the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan and Brown University, USA as a senior research associate, respectively. In early 2013, he joined Shanghai University as a professor. His current research interest focuses on the fundamentals and multiscale calculation of electrochemical energy storage materials and materials design and performance optimization using machine learning.